- Framework
- Authentication & Authorization
Framework
Authentication & Authorization
Authentication & Authorization, JWT, RBAC
Authentication
JWT
Authorization
How to check the authorities of a login account, you need 3 steps:
- define a resource(API path)‘s authorization properties
- login account security context customization
- setup the account and authorities mapping
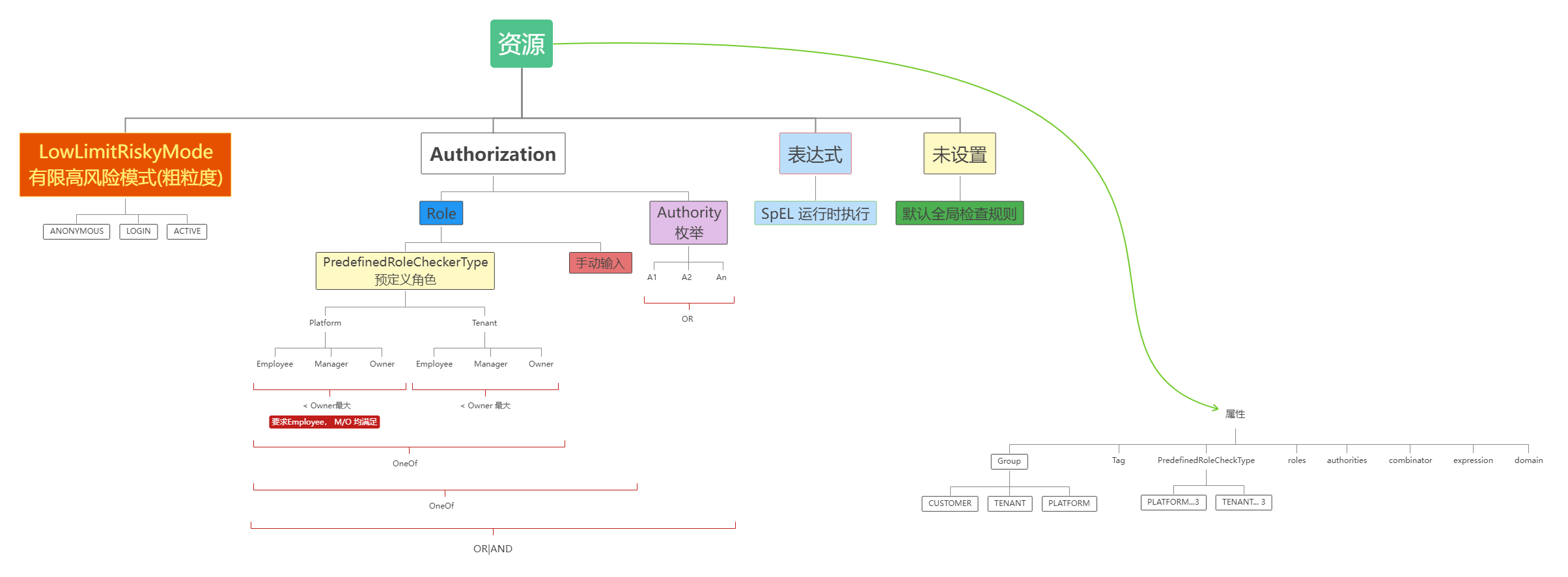
Define resource authorization
check Milestone 20240510 rbac part:
1. Setup the authority enum
enum BookAuthorityEnum {
option (hope.swagger.enm) = {
description: "Authority used in book project"
};
BOOK_ADD = 0 [(hope.constant.field) = {code: 1,message: "book:add", message2: "Authority to add book"}];
BOOK_DELETE = 1 [(hope.constant.field) = {code: 2,message: "book:remove", message2: "Authority to delete book"}];
BOOK_MODIFY = 2 [(hope.constant.field) = {code: 3,message: "book:modify", message2: "Authority to modify book"}];
}2. update the hope-wire.json of the proto module
"authority" : {
"enumClass" : "com.novel.book.proto.infra.settings.BookAuthorityEnum",
"codePrefix" : 10240000
}3. protect your resource
rpc ListCategory (com.novel.book.proto.api.admin.request.CategoryListRequest) returns (com.novel.book.proto.api.admin.response.CategoryVoResponse) {
option (hope.swagger.operation) = {
get: "/list-category";
description: "list all the categories support";
priority: MIDDLE;
out_plural: true;
authorization:{
rbac:{
authorities: "BOOK_DELETE";
combinator: OR;
predefined_role_checker: PLATFORM_MANAGER
}
}
};
}4. runtime configuration
Those configuration will happen on your application module instead of the proto module:
find the auto generated code template at your application project’s package : ${PKG}.infra.security (domain as Book example):
1. AnonymousBookCustomer.java
2. BookCustomer.java
3. BookJWTPicker.java
4. BookQuickCustomerRoleChecker.java
5. BookSecurityCustomerContextCustomizer.java
6. BookSecurityCustomizer.java| Class | Usage | Comment |
|---|---|---|
AnonymousBookCustomer | Anonymous Customer definition | usually no need to update |
BookCustomer | Customer used in the security context | extend for additional fields for dynamically loaded, like authorities, usually BookSecurityCustomerContextCustomizer response for init and wrapper it, need extend |
BookJWTPicker | Where to pick the JWT | usually from header, but you can pick from session or cookies |
BookQuickCustomerRoleChecker | Quick Platform\Tenant role checker | usually need to extend |
BookSecurityCustomerContextCustomizer | response for Security context customer initialization | more detail info to/from token, create new Customer like delegate authorities/role fetcher |
BookSecurityCustomizer | Security configuration customize | change global security strategy: like default access check, or specific rule for specific path |
5. Last piece
This is not what the framework can supply as this depend on your business logic: how to set up your account relationship with the authorities list.
Best practice is to follow the role based access control that is RBAC.
SO you may leverage the Authority Enum for example BookAuthorityEnum’s message pattern to organize your authorities hierarchy:
Take this book application as example:
BOOK_ADD: book:add
BOOK_DELETE: book:delete
USER_BLOCK: user:block
USER_EDIT: user:edit
ORDER_APPROVE:order:approve
ORDER_DELETE:order:delete
ORDER_MODIFY:order:modify
so the hierarchy may looks like:
+---book
| add
| delete
|
+---user
| block
| edit
|
+---order
| approve
| delete
| modify
㊗️ so enjoy!
Disable Spring Security
️️⚠️ Apihug Security is not compatible with Spring Security at runtime.
The simplest way to disable Spring Security is to remove its dependency from the project.
By doing this, we’ll remove all security-related configurations and defaults provided by Spring Security:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
<version>...</version>
</dependency>Removing this dependency eliminates all Spring Security features from the application.
But if you want leverage some Spring security components, we recommend you to disable the spring security autoconfiguration manually:
Excluding Spring Security Auto-Configuration
Spring Boot automatically configures security when we include spring-boot-starter-security in our classpath. To disable it, exclude the auto-configuration by adding the following property to application.properties:
spring.autoconfigure.exclude=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfigurationIf we want to disable Spring Security completely, we should use spring.autoconfigure.exclude without creating a SecurityConfiguration class.
Manually configuring the Spring Security class overrides the application.properties configuration, so exclusion in the application.properties has no effect when both are used together.